Problem : 거의 최단 경로
유형 : 다익스트라
문제 해석
- 최단 경로에 해당하는 경로를 피하고, 목적지에 도달하는 두번째 최단 경로를 찾아라.
문제 재해석
- 한 점에서 부터의 최단 경로를 구하는 문제이다.
다익스트라로 해결이 가능하다.
해결 전략
- 단순히 최단 경로를 하나를 구하는 것은 쉽다.
- 하지만, 최단 경로가 여러개인 경우를 처리해 주어야 한다.
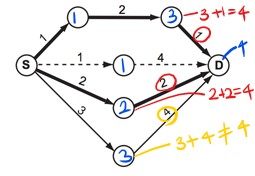
- 이것을 해결하기 위해, 도착점 부터 시작점 까리의 가중치를 역추적 해나간다.
목적지 지점까지 소비한 비용과목적지 이전 지점 까지 오는데 소비한 비용+목적지 이전 지점에서 목적지까지의 경로 이동 비용을 비교한다.- 만약 두 값이 같다면, 해당 경로는 최단 경로가 된다.
설계
- 다익스트라를 통해 목적지 까지의 최단 경로 가중치를 구한다.
- BFS 를 통해 목적지부터, 시작점 까지의 가중치를 비교해보면 거슬러 올라간다.
- 만약 최단 거리에 해당되는 경로를 찾았다면, 해당 경로를 지운다.
구현
- 두가지 방법으로 구현하였다.
첫번쨰 방볍
- vector 를 이용하여 인접 리스트를 만들고, 각 정점 끼리의 가중치를 관리하는 인접 행렬을 두고 관리했다.
두번쨰 방법
- 장소의 수가 500이다. 즉, 모든 장소들끼리 연결되어 있어도
500P2밖에 되지 않는다. - 이점을 이용하여, 도시 간의 관계를 바로 인접 행렬로 관리하고, 최단 경로의 경우 INF 값을 주어 삭제 하였다.
주의할 점
- 최단 경로가 여러개일 수 있고, 그 최단경로가 중복되어 사용 될 수 있다.
- 예시를 들어보겠다.
1이 출발지 ,5가 목적지 일때
1 | |
- 위와 같은 경우, 첫번 3 > 5가 중복되는 경우를 처리해야한다.
- 단순히 첫번째 다익스트라를 통해 나온 경로를 방문 표시 해버린다면 3 > 5 가 방문 표시되어 1 > 4 에 대한 처리가 되지 않는다.
- 비교하는 과정에서 INF를 더해 발생하는
overflow를 조심해야 한다.
첫번째 방법 코드
1 | |
두번째 방법 코드
1 | |
디버깅
- 주의할점 에서 언급한 내용을 놓쳤었다.
피드백
BFS를 통해 최단경로를 다 찾는법을 배웠다.- 요새 밤에 푸는 문제가 더 잘 안 풀리는것 같다.
- 첫
WA를 받고 문제점은 바로 찾았으나, 아이디어를 내가 싫어, 자고 일어난 뒤 다시 시도하니 금방 풀렸다..